Many businesses are moving away from traditional phone systems in favor of new technologies like VoIP. While POTS (Plain Old Telephone Systems) are known for their call quality and reliability, they can be disrupted by natural disasters that affect phone lines. Cellular technology also has a good call quality if used within the range of a cell tower. Delay, Jitter, and Packet Loss
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technology where voice travels in data packets to relay signals via Internet calling. The call clarity and responsiveness in VoIP calls are crisp and clear, and the Businesses can hear customers’ words.
Monitoring call quality ensures the quality stays strong over time, and the customer will maintain brand loyalty. The right cloud-based phone system will help get good VoIP phone quality and software integrations that will enhance the customer experience.
Factors Contributing To Delay, Jitter, And Packet Loss
The quality of VoIP calls can be measured depending upon the network environment.
Various factors could be the reason for this. Even delay, jitter and packet loss could cause issues for VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) phone calls, and it is necessary to reduce these as much as possible for a smooth call. A few factors that contribute to delay, jitter, and packet loss include,
Old networks with outdated hardware equipment like cables, routers, or switches could be a good reason for jitters. Even jitters can be felt while using a wireless network due to the network connection being of low quality.
When packets get sent toward the destination computer over the network using an IP phone or even VoIP service, there sometimes happens a delay. This delayed packet may or may not arrive at all at the destination and in this case, it is lost and the main reason for it is the primary network issues.
Packet loss occurs When the data travelling between the PC and the server is lost along the way. It could be due to a faulty ethernet cable, issues in the network interface controller, outdated firmware in the router, network congestion, and others. Critical Factors Affecting User Experience:
Jitter
Jitter is a VoIP call quality problem concerning the timing of delivery of data packets to the receiving party. The data packets arriving at the destination arrive late or at irregular intervals, and the voice sounds to break up, making it most difficult to hear the words said.
Managing Jitter In VoIP Communication
The time delay between relaying and receiving data packets over any network is jitter. VoIP calls face jitter when the communication link has conflicting delays in sending and receiving the data packets. A few reasons for the same include,
- Routing issues
- Limitation of the existing hardware
- Congestion in the network
- Interferences that occur in the network
Testing Jitter On VoIP Phones
Jitter is the usual suspect when the call quality on a voice communication drops and a bumpy sound arises. Until a jitter test is done, the exact issue cannot be found. Nearly all the networks diagnose jitters in milliseconds. One can determine jitter levels by running various tests like
- Online speed test
- Use a network monitoring tool
- Measuring jitter manually via terminal-based ping test
Fixing VoIP Jitter Issues
When VoIP jitter is established as the main problem behind the issues in the quality of the calls made, a solution can be worked upon to mitigate this voice problem. A few of the steps involved in fixing jitters are,
Use A Wired Internet Connection
Calling via Wi-Fi can face interference from electrical motors and microwaves. If the users make call face jitters in the afternoon, especially during lunch breaks, it usually is due to environmental causes, and if it occurs during peak business hours, it has something to do with the device frequency. It could also mean an intervention from another wireless device using the same band frequency.
Upgrade Internet Connection
If the VoIP user is experiencing jitters every other day then it is a cue to upgrade the internet service plan to provide higher download and upload speeds. This will help in supporting more devices that can easily handle VoIP traffic without risking jitters.
Testing Connections Issues
This approach finds the exact cause of high latency in VoIP quality, and checking the settings has a limit. Making use of network diagnostic tools helps in keeping tabs on the issues regarding jitters. Running tests at different times in the day helps in knowing the specific periods when it is at its peak.
Jitter Buffer Setting Up
When there exists a continuous jitter, then a buffer could be set up to accommodate this jitter. This jitter buffer works by holding up the VoIP audio just right enough to rearrange voice packets correctly.
Adaptive Jitter
The adaptive buffer helps monitor those conditions experienced during the transmission of the latest voice packets and automatically increases or reduces the buffer size.
Quality Of Service Enabled
It refers to those technologies that help in controlling the overall performance of the existing user network. Here, the settings can be configured to categorize the VoIP packets that allow the VoIP calls to proceed through all types of queues.
Even if downloading around 20 huge video files in a shared co-worker’s office, the packet prioritization in the settings option will ensure that the voice packets never get held up.
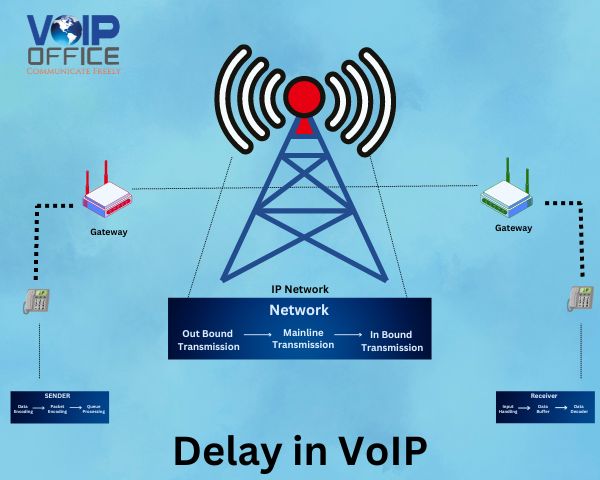
Delays
The conversations that go back and forth get delayed, or when the user hears echoes that break the flow of the conversation.
In VoIP phone communication systems, voice latency is slightly delayed as audio data moves from one phone system to another. Due to this delay, the person on the other end of the line will hear the talker after a few milliseconds. This causes flaws in the audio data.
Components In Delay
Delay in VoIP is the latency, distinguished as the amount of time it takes the voice to come out of the speaker’s mouth and the time it takes to reach the listener’s ear. A few components in delay are,
Propagation Delay
The Light travels at a speed of 186,000 miles per second through a vacuum, whereas the electrons travel at 125,000 miles per second, approximately through copper or fibre. The fibre network that stretches 13,000 miles around the world induces a one-way delay of 70 milliseconds. This delay is almost undetectable to the human ear. The propagation delays that co-exist with handling delays cause speech degradation.
Handling Delay
Handling delay, known as processing delay, defines the cause for delay, be it actual packetization, compression, or packet switching. These delays are found to be more in packetized environments.
Queuing Delay
There are many reasons for delays in network experiences. These are the times needed to move the actual packet to the output queue, known as packet switching, which leads to queuing delay.
Packets are held in a queue because of the bottleneck on an outbound interface, resulting in queuing delays. These delays occur when more data packets get sent out than the interface can handle at any given interval.
Weak Internet Connection
The VoIP call mainly relies on the availability of the internet, which receives and sends voice signals across. A weak internet connection disrupts calls, which could be lost altogether. Compared to general home internet, VoIP calls require a different set of protocols.
Insufficient Router Bandwidth
Usually, small businesses use only one router for voice data as it is properly configured to give importance to voice call-over data. A high-end router with greater bandwidth is a good solution.
Configuration Of Internet
VoIP calls use a different set of call protocols that are different from home internet. The proper VoIP configuration improves call quality.
Latency In Communication Channel
Latency is the delay that occurs when the data is sent and received over a network or any given communication channel. I refers to a minimal delay crucial for smooth, flawless real-time communication.
Importance of Low Latency In Real-Time Communication
- Low latency is a fault in real-time communication, as delays can be dangerous.
- Like in finance, a few milliseconds could make a significant profit or loss in high-frequency trading.
- Meanwhile, low latency ensures a flawless gaming experience, whereas a delay will cause the game to lag or freeze.
- Low latency is crucial for telehealth and remote consultations in the healthcare industry. Delays in effective communication can cause misunderstandings of medical symptoms that will lead to wrong diagnoses.
- Low latency is essential for telecommunications as it involves real-time voice and video calls, and any delay in communication could make the situation difficult.
Mitigating Delay In VoIP Calls
In telecommunications, latency or delay is the total time taken between when a person speaks and when the other person at the other end of the line hears that voice. It will be challenging to conduct conversations if the delay in VoIP calls is relatively high.
Strategies for mitigating delay are,
Upgradation Of Slow Networking Equipment
Network traffic-based applications like voice or video traffic should be prioritized. Invest in a VoIP priority router to download large files over a call, as large files could impact the quality of the call. Upgrading the network equipment will ensure proper network optimization.
Improve data pack routing
If the data packets have to make two or more unnecessary journeys to reach the destination, then routing has to be improved.
Select the right Internet Service Provider (ISP)
Ensure the internet connection has adequate bandwidth for calls during network use. When using around ten phones at a time, it is advisable to have a business-class service for VoIP traffic.
Quality Of Service (QOS)
It is a set of technologies that work on any given network, guaranteeing its ability to depend on high-priority applications and traffic under limited network capacity. Qos technologies achieve this by providing various capacity allocations to handle specific flows in network traffic.
Quality of service technologies accomplish this by providing differentiated handling and capacity allocation to specific flows in network traffic. This enables the network administrator to assign the order in which packets are handled and the amount of bandwidth afforded to that application or traffic flow.
Error Correction
Error detection is used to check if the call receiver correctly received the data or corrupted data. Whereas Error correction is used to correct errors detected when the data gets transmitted from the sender to the receiver.
Forewarned Error Correction (FEC)
A well-known technique for controlling errors during the transmission of data. In the internet protocol networks, the errors translate into a loss of a UDP (User Datagram Protocol), due to which FEC is referred to as forward erasure correction. One of the main goals of FEC is to revive the lost packet, which is based on packets that are transferred along with the unessential information that gets included in specified FEC packets.
Voice Redundancy
It is a process of designing a phone system that remains operative even at the time of the natural disaster, as the redundancy plan,
- Technology is purely cloud-based.
- The support teams and system servers are spread in multiple locations.
- Timely backup of servers along with proper backup power.
- Multiple phone lines.
- Routine strategies for backup.
As far as phone systems are concerned, redundancy is achieved by using only the VoIP technology. These Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems make use of an internet connection to make and receive the calls. Since this technology is based on cloud communication it is not particularly tied down to a specific location or even a device.
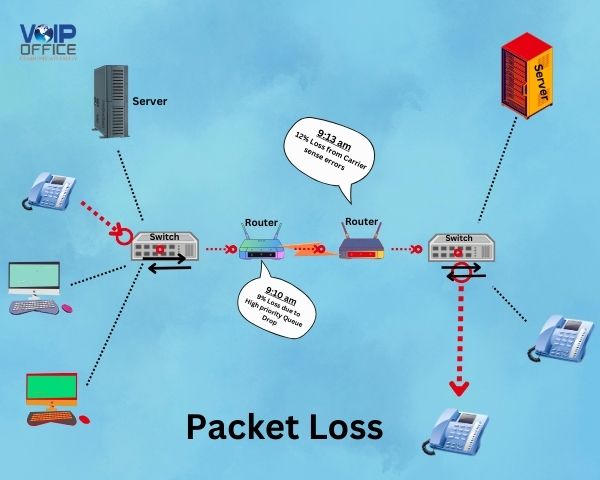
Packet Loss
When pieces or “packets” of data travelling over a network do not reach their final destination, it is known as packet loss. The packets failing to get to the other end of the communication on the network leads to missing data. In VoIP calls, missing data pieces constitute missing conversation, which isn’t ideal for calls.
Reason For Packet Loss
When there is a loss of data packets in transit or even when these packets get delayed on arrival, it results in poor quality issues on the VoIP software during calls. There are different causes for packet loss, which are usually unplanned and unintentional. A few of these are,
Congestion In Network
This is one of the main reasons for VoIP call packet loss in most data transfers. One can imagine a network like a freeway where vehicles are plying, and these vehicles are the packets. When traffic jams occur, high congestion happens on the highway. The packets get slowed down as most get jammed into single lanes, just like a traffic jam, which causes congestion.
Network Hardware
If the hardware used in the network is not good enough, then there will be packet loss and connectivity issues during the call. Hardware devices like modems, network switches, computers, and routers should have up-to-date VoIP abilities to reduce packet loss, which in turn delivers premium call quality.
Overloaded devices
When any given network operates higher than it can handle, it gets weakened and becomes weak enough to process all the data packets simultaneously, which causes a few of them to get dropped. Many devices have buffers built inside them to hold the assigned packets until they are sent.
Bandwidth Loss
There will be a loss of bandwidth whenever there is trouble in the network apart from the congestion. Like during heavy storms, when there is a power outage, the public tries to compete for the remaining available power. This scenario will lead to latency, packet loss, and additional issues with voice calls.
Less Speed
Running a modern VoIP system on outdated hardware or software can reduce speed and hinder packet delivery. Since speed is crucial for successful VoIP calls, upgrading to a suitable business-class internet plan may be necessary if current speeds are insufficient.
Packet Loss In Wi-Fi & Wired Networks
Wireless networks are more exposed to packet loss than wired networks. Issues due to weaker signals, radio frequency interference, and physical barriers like walls, among others, cause the Wi-Fi networks to drop the packets.
In wired networks, the culprit could be faulty cables that could hinder the flow of the signal through the cable.
Software Bugs
Software bugs or security threats can also cause packet loss. Thoroughly test systems and address all potential issues to identify and resolve the root causes.
Consequences Of Packet Loss
The consequences of packet loss on voice quality cause mangled or even choppy audios, which could lead to breakdowns in communication along with misconceptions. Even a minute amount of packet loss creates distinguishable disturbances, which makes the callers and the listeners face tremendous challenges during the flow of the conversation.
As the length of the conversation continues, it becomes shattered with gaps or even words missing in the lengthy dialogues. The callers will experience many delays and need to repeat the conversation sections, decreasing the overall call experience.
For those video calls that use WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) technology, packet losses will affect both the visual and the audible aspects of the communication. Video call users will experience blurry images and frozen frames in their video feed as the data packets are missing.
Consistency in the audio clarity will decrease as the audio heard will be disarrayed with the video. This will create significant clarity in video streaming, leading to anxious movements, which degrades video quality.
The volume of increased packet loss will frustrate the users and considerably hinder proper communication and collaboration during calls in online meetings. This is a problem in those scenarios where non-verbal signs and optical information are vital for more successful interactions, like in remote consultations or educational sessions.
This is problematic in scenarios where non-verbal cues and visual information are vital for effective interactions, such as remote consultations or educational sessions.
Packet Loss And Call Clarity
Audio or video data is split into unique packets and scrambled before being sent to its destination. At the receiving end, it is deciphered and reassembled into a coherent message. As packet loss is present, it creates a negative impact on the call quality.
Addressing Packet Loss In VoIP
For many users, packet loss manifests as slow document downloads, frozen videos, or distorted VoIP calls. Increased packet loss reduces the amount of data transmitted through a network connection.
Packet loss affects different types of applications diversely. Packet loss may not trouble users when it is the question of a simple type of document download. Like a packet loss of 10%, that takes an extra second while downloading a 10-second document will not cause much irritation.
Latency, which includes packet loss, refers to delays in processing network data. Even a 2% packet loss can be noticeable, causing issues like poor video streaming or degraded voice call quality.
Causes For Packet Loss
- Congestion in the existing network
- Problems in the Network Hardware
- Bugs in the software
- Threats that may cause a security breach
- Devices overloading on a network
- Wireless and wired networks
- Fault in network configuration
Fixing Packet Loss
Zero packet loss is unattainable; you can only reduce packet loss percentages due to unavoidable factors like system overload. A few tips to fix packet loss are,
- Restart the existing system
- Verify that network connections are properly configured.
- Using wired connections instead of routing Wi-Fi connections.
- Upgrade the existing software.
- Replacing the old hardware.
- Making use of quality-of-service settings.
- Strengthening the system security.
Measuring And Monitoring VoIP Quality
VoIP quality is the all-inclusive audio along with visual performance that the user experiences while using Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) calls. Many factors including signal strength, call clarity, echo, and delay including audio and visual will impact the users’ experience.
Factors that influence VoIP quality,
- Device used for call
- Network framework supporting the call
- Internet connection
Measuring VoIP Quality
Measuring and monitoring the quality of VoIP ensures that users can communicate competently and successfully without experiencing infuriating audio or even visual interruptions.
By measuring call quality effectively, VoIP service providers can identify areas for improvement. They can then take the necessary steps to enhance the quality of their service.
MOS score
Mean Opinion Score (MOS) is a personalized metric where a group of people rates the quality of audio samples. The telecommunication industry widely uses MOS scores to assess VoIP call quality.
R-factor
It is a biased metric that measures the quality of VoIP calls. Many factors like delay, jitter, and packet loss produce a score between 0 and 100. As the R-factor achieved is higher, so does the quality of the call
Packet loss
The packet loss rate is the voice packet percentage lost during data transmission. A higher packet loss rate leads to poor call quality.
Jitter
It is the variation of delay that happens in between packets. The higher the jitter is, the quality of the call deteriorates.
Latency
Delay occurs between sending and receiving voice packets. High latency significantly degrades call quality.
Echo
Echo, where a caller hears their own voice through the earpiece, is caused by inadequate echo cancellation, network delays, and other factors affecting call quality.
Mostly Used Monitoring Techniques For VoIP
Monitoring VoIP uses various methods to ensure exhaustive monitoring of its systems. Mainly used techniques include,
Active Monitoring
It involves simulating VoIP traffic by generating test calls to measure and assess call quality, focusing on metrics such as jitter, latency, packet loss, and MOS score. This type of monitoring helps in evaluating performance and troubleshooting.
Passively Monitoring
It involves inspecting and capturing the traffic in the network to extract applicable VoIP-related data. Without actively generating the test calls, it helps monitor live VoIP sessions and recording packets without diligently generating test calls.
Call Detail Record (CDR) Analysis
VoIP systems also can generate detailed call records that have information on each call made, including parties involved, call duration, call quality metrics, and other factors. This provides valuable insights into patterns of the call made, statistics of the quality of calls made, and helps identify specific issues related to calls made.
Protocol Analysis
It analyzes VoIP protocols, like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol), and others. The help of examining protocol details, including media streams, signaling messages, and codec usage, helps to analyze protocol that helps in diagnosing call setup issues, negotiation of media, and performance of codec.
Quality Of Service (quality of service) Monitoring
It helps monitor and analyze network performance to ensure adequate bandwidth, prioritize VoIP traffic, and maintain call quality.
Testing End To End
This testing involves managing thorough rests that easily mimic the VoIP real-world scenarios. This process assesses call quality and evaluates network performance across the entire VoIP infrastructure, including devices, network segments, and endpoints. This will help identify misconfigurations, bottlenecks and other quality issues that may arise in the system.
Best Practices For VoIP Call Quality
Most businesses choose VoIP calling because it gives much more than normal voice calling. It helps in integration to smartphone apps seamlessly which works both on mobile devices and even on desktops. It also has collaboration capabilities like video conferencing and whiteboarding. A few best practices for VoIP call quality include,
- Increase the network bandwidth.
- Upgrade the existing router.
- Increase bandwidth to prevent congestion.
- Selecting the right codec.
- Configure quality of service.
- Setting up a jitter buffer.
- Switch from Wi-Fi to Wired internet connection.
- Always prioritize VoIP calls over the network connection.
Conclusion
Delay, jitter, and packet loss, troubles voice quality in VoIP calls. Addressing these factors effectively is crucial for a seamless voice-calling experience. Maintaining VoIP call quality requires regular monitoring and proper system configuration. The other factor in VoIP technology is redundancy in the system, as it has no geographical restrictions.
Even if one server or one location’s connection goes down, the user of VoIP services can easily switch to another server or location without any interruptions in the ongoing services. Error correction techniques help streamline the impact of delay, jitter, and packet loss on VoIP Calls.
To mitigate the effects of delay, jitter, and packet loss on VoIP calls, consider upgrading old hardware, increasing internet bandwidth, and exploring other available options.

Pingback: Are VoIP Calls Secure? -
Pingback: Area Code 901 phone number - Memphis -
Pingback: Area Code 205 phone number – Birmingham -
Pingback: Area Code 561 phone number - Boca Raton -
Pingback: Area Codes 312, 773, and 708 phone numbers – Chicago -